How Does a Speaker Work?
The cone is the most visible portion of a speaker and is the only portion that needs to move up and down. The movement of the cone pushes the air, generating high and low pressure. This is what creates sound waves.
These waves would be quite similar to the electrical wave that was transmitted to the speaker in the first place.

Does speaker size matter?
Because the ratio between the mass of air pushed through and the magnet strength is low, small speakers are better at transients (quick changes in frequency) and volume changes.
What distinguishes large speakers from smaller ones, is the capacity of reproducing low frequencies. A large cone can move large amounts of air and produce low-frequency waves.
How much power does a speaker use?
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipiscing elit. Blandit quis suspendisse aliquet nisi sodales consequat magna. Sem placerat in id cursus mi pretium tellus. Finibus facilisis dapibus etiam interdum tortor ligula congue.
Is the speaker cabinet only decorative?
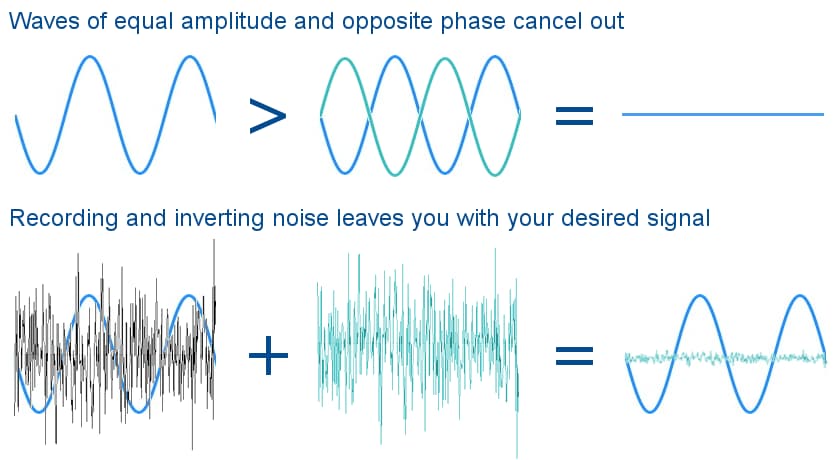
The term "cabinet" refers to the enclosure in which a loudspeaker is installed. The enclosure's main purpose is to keep rear “negative phase” sound waves from combining with “positive phase” sound waves from the front. Otherwise, cancellation and interference patterns would occur, compromising the speaker's efficiency and sound quality. The ideal cabinet would dampen the rear sound completely.
Purpose of A Speaker Vent
A resonant frequency is a natural frequency of vibration determined by the physical parameters of the vibrating object. The vent/port is there to improve the enclosure's bass response characteristics, which is typically done by generating a controlled resonance of the air at a frequency just below the speaker's normal cutoff frequency in the given enclosure. The internal volume of the box and the port are key to defining the resonance frequency.
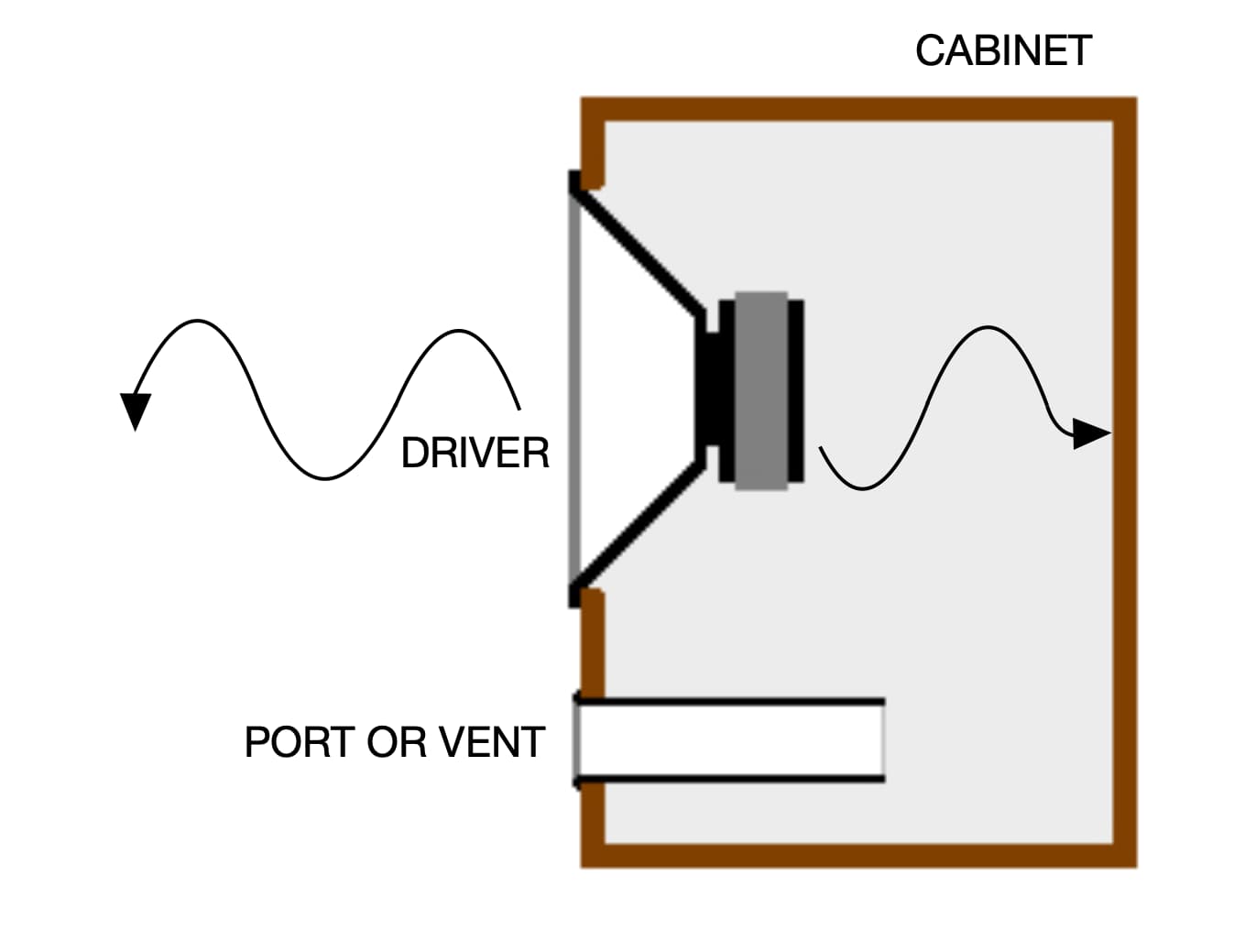
What occurs when the size of the cabinet is altered:
- Enlarging the cabinet lowers the resonant frequency
- Reducing the cabinet size increases the resonant frequency
For any given port diameter, what occurs when the length of the port is altered:
- Elongating the port lowers the resonant frequency
- Shortening the port increases the resonant frequency